In recent years, headlines have been filled with stories of workers from various industries on strike and attempting to unionize. The roots of these efforts lie with workers in the 1800s and early 1900s who first attempted to organize and used strikes to protest low wages and poor working conditions. Those early labor movements contributed to the passage of the National Labor Relations Act (NLRA) of 1935, which gave workers the right to organize into unions and made it the official policy of the US to encourage collective bargaining. Although union membership surged after its passage, the NRLA had less of an impact for women and people of color, whose main occupations in agricultural and domestic work were deliberately excluded from the law, exclusions that still negatively affect millions of workers today. And the impact of NRLA in supporting collective bargaining has also waned over time, as membership declined from 35% of wage and salary workers in 1954 to just 10% in 2022. As panelists discuss in this event, the future of work and job quality rests in part on workers having the ability to influence their work and workplace, and the NLRA provides the legal foundation for workers’ right to exercise that agency. As we look to shape the future of work, what lessons can we learn from the NLRA’s history, impact and effectiveness today?
Overview
Issue Areas
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Enter your email address below to receive updates from the Job Quality Center of Excellence and related job quality news from the Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program.
Related Resources
The Resource Library is the heart of the Job Quality Center of Excellence. Check out our recent
additions below, and click “View All Resources” to explore more.
Event2025
How Good Jobs Support Small Business Success: Lessons from the Shared Success Demonstration
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program
Event2025
Working and Homeless in America — A Book Talk with Brian Goldstone
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program
Event2025
Driving the Economy: The Essential and Undervalued Work of Truckers
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program
Event2025
Re-Entry and Good Jobs: Building the Second Chances We All Believe In
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program
Event2025
A New Year’s Resolution to Reject Over Work — A Book Talk with Brigid Schulte
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program
Event2025
Workplace Democracy: Sharing Power and Decision Making at Work
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program
Event2025
Community Benefits Agreements: A Tool for Creating Good Jobs
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program, et al.
Event2025
A Hidden Workforce: Prison Labor, Human Rights, and the Legacy of Slavery
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program
Event2025
Seizing the Moment on Worker Rights: A Toolkit for Organizers and Practitioners
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program, et al.
Event2025
Tapping into Worker Voice to Improve Job Quality: Lessons from the Talent Pipeline Management Network
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
The Workers Behind Our Groceries
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program, et al.


Event2024
The Guarantee
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2025
Employee Ownership Ideas Forum 2024
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program, et al.


Event2024
Workers On the Line
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program, et al.


Event2024
Job Quality in the Fields
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program, et al.


Event2024
The Alternative
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program



Event2024
How Benefits Make Jobs Better
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Reimagining the Business-Labor Playbook for the 21st Century
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Unstable Schedules
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Sustaining Ownership
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Wealth Supremacy
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Good Work in the Gig Economy
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Employee Ownership Ideas Forum
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program, et al.


Event2024
The Case for Good Jobs
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
ESOPs, Job Quality, and Wealth Inequality
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Still Broke
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
The Promise of Guaranteed Income
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
The Great Escape
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Economics Reimagined
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program, et al.


Event2024
Procurement with Purpose
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Democratizing Work
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Ownership at Work
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Opportunity by Design
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
For Better or Worse
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
A Workers’ Bill of Rights
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program



Event2024
The Occupational Safety and Health Act
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2025
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program
Event2024
The Future We Need
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
The Rewards of Work
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Worker Power and the National Labor Relations Act
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Essential Jobs, Inequality, and “Dirty Work”
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program



Event2024
Toward Universal Work-Related Benefits
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Insights from Businesses
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Worker Financial Wellness
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Encouraging Job Quality in Small Businesses
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Valuing Care
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program



Event2024
How 2020 Accelerated Digital Transformation at Companies and What That Means for Frontline Workers
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program



Event2024
California’s Plans for the Future of Work, Workers, and a Renewed Social Compact
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program
Event2024
A Job Quality Agenda to Build Back Better
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Moving Beyond Gratitude
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Can Investing in Workers Support Small Business Resiliency Through the Pandemic?
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2025
Can Employee Share Ownership Improve Racial and Gender Wealth Equity?
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
How the Workforce System Can Advance Workplace Health and Safety During and After the Pandemic
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
California’s Approach to Recovery and Resilience
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Open to Good Jobs
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Increasing Equity in a Post-Pandemic Economy
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Race, Economy, and COVID-19
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Job Quality in the Age of COVID-19
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
How Can Workforce Leaders Boost Job Quality?
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
To Boost Job Quality, Money Matters
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Measure What Matters
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Assessing Job Quality and Equity in Your Local Labor Market
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Demanding Dignity at Work
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Quality Jobs for All
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Opportunity Zones and the Challenge of Addressing Our Economic Divides
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
The Rise of Gig Work
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Fresh Pathways
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
The Aspen Institute Launches New Tool to Create Business Incentives by Measuring Good Jobs
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
The Justice System and Jobs
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Having a Stake
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Drivers of Opportunity
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
I Am Not a Tractor
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
What’s in Store


Event2024
Race, Work, and Opportunity in America
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
The Caring Economy
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Building Good Jobs into America’s Infrastructure Investments
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Launch of the Good Companies/Good Jobs Initiative
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Has the First Job Disappeared?
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Building Ladders and Raising the Floor
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Democracy at Work
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Finding Time
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Can Inclusive Economic Development Build Better Jobs and a Stronger Regional Economy?
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Shop ‘til Who Drops?
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
The 1099 Economy


Event2024
The Future of Worker Voice
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
The Future of Work in the Sharing Economy
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Beyond Great Places to Work
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Getting to Work
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program



Event2024
The Low Cost of Good Jobs
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Time to Care
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Book Talk on The Good Jobs Strategy
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program
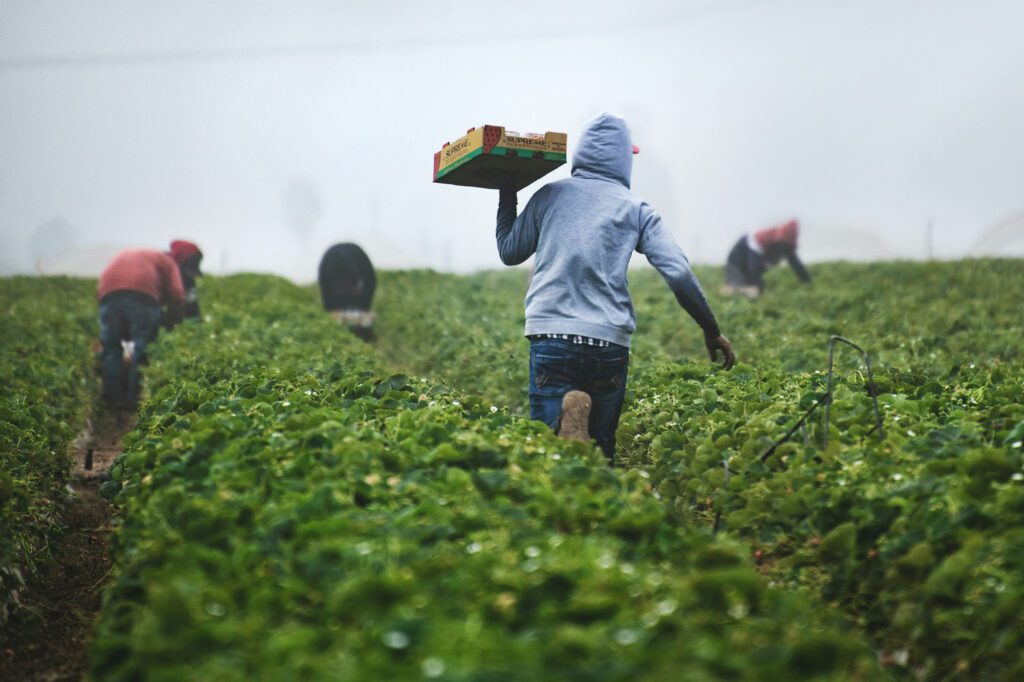


Event2024
Experiences of Immigrant Workers
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Leaning in with Child Care
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Raising the Minimum Wage
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Home Economics
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
From Jobs to Job Quality
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
The Housing Market’s Foundation
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
Taking Inventory of Retail Jobs
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program, et al.


Event2024
Better Care through Better Jobs
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program


Event2024
From Fast Food to Fine Cuisine
The Aspen Institute Economic Opportunities Program
Submit a Resource
What resources have you found useful for advancing job quality? Share your favorites so we can consider adding them to the Job Quality Center of Excellence.
Submit A Resource